- Cleaning, Decontamination and Sterilization
Essential infection control processes
Avoid the transmission of infection to patients from medical equipment and surgical instruments

- Overview
- Cleaning, Decontamination and Sterilization
- Environment Cleaning and Disinfection
- Needles, Syringes and Sharps Safety
- Surgical Site Infection Prevention
- Universal/Standard Precautions
Sterilization & the Spaulding classification1, 2, 3
Procedures involving contact by a medical device or surgical instrument with a patient’s sterile tissue or mucous membranes pose a risk for the introduction of pathogens that can lead to infection. To help lower this risk, the CDC recommends practicing decontamination and sterilization as part of any infection prevention program and promotes the Spaulding classification to determine risk.
The CDC defines the Spaulding classification as a strategy for the sterilization or disinfection of inanimate objects and surfaces based on the degree of risk involved in their use. The three categories are non-critical, semi-critical and critical and they describe three levels of germicidal activity for disinfection (high, intermediate and low).
Non-Critical Surfaces Under the Spaulding Classification
Non-critical devices include those that contact intact skin but not mucous membranes. Secondary transmission may occur through contaminated hand/glove contact with the environment and transfer to the patient/resident. These devices require low or intermediate level disinfection. Low and intermediate level disinfectants include ethyl or isopropyl alcohol, quaternary ammonium (QUAT), QUAT with alcohol, hydrogen peroxide, chlorine, phenolics and iodophor.
Non-critical surfaces under the Spaulding classification
Non-critical devices include those that contact intact skin but not mucous membranes.
Secondary transmission may occur through contaminated hand/glove contact with the environment and transfer to the patient/resident. These devices require low or intermediate level disinfection.
Low and intermediate level disinfectants include ethyl or isopropyl alcohol, quaternary ammonium (QUAT), QUAT with alcohol, hydrogen peroxide, chlorine, phenolics and iodophor.
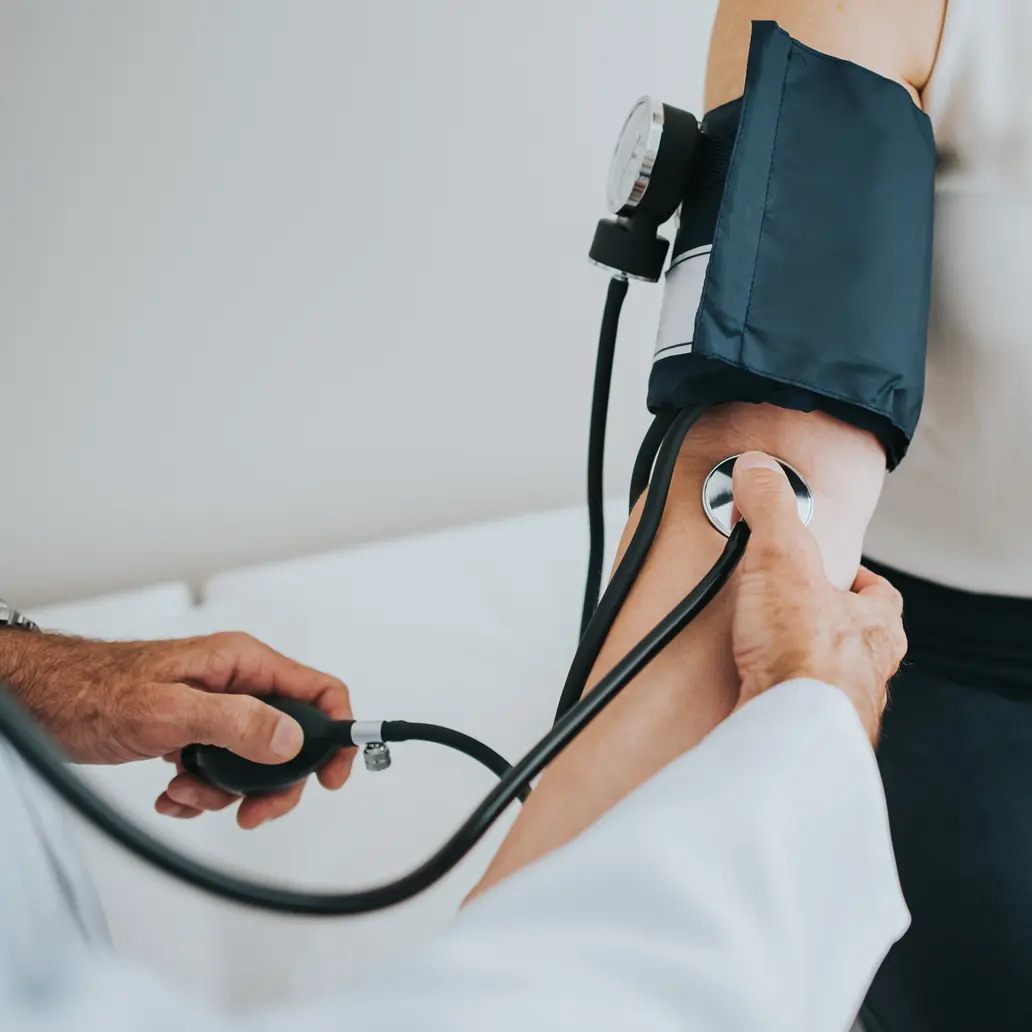
Low-level disinfection
Low-level disinfectants are used to disinfect noncritical items that come in contact with skin, such as stethoscopes, blood pressure and tourniquet cuffs, EKG leads, bedside equipment and environmental surfaces.
Low-level disinfection kills most vegetative bacteria, some viruses and some fungi, but cannot be relied on to kill mycobacteria or bacterial spores.
Intermediate-level disinfection
This procedure kills vegetative bacteria, most viruses and most fungi – including mycobacterium tuberculosis, all fungi and inactivates most viruses – but does not reliably kill bacterial spores. Appropriate for items such as stethoscopes, x-ray machines and bedside rails.
Intermediate disinfection is also part of environmental cleaning in healthcare facilities and includes housekeeping surfaces like floors, lighting, walls, overbed tables and carts. Cleaning frequency is dependent on high-touch areas, spills, soiled surfaces and patient care items.
Point-of-care device cleaning
Point-of-care cleaning describes the process that eliminates many or all pathogenic microorganisms, except bacterial spores, on inanimate objects.
Point-of-care devices like glucometers must be adequately cleaned and disinfected between patient use. Review manufacturer’s instructions for use (IFU) for cleaning procedures of the device.
Semi-Critical Surfaces Under the Spaulding Classification
Semi-critical objects are those that touch mucous membranes or skin that is not intact and require a high level of disinfection.
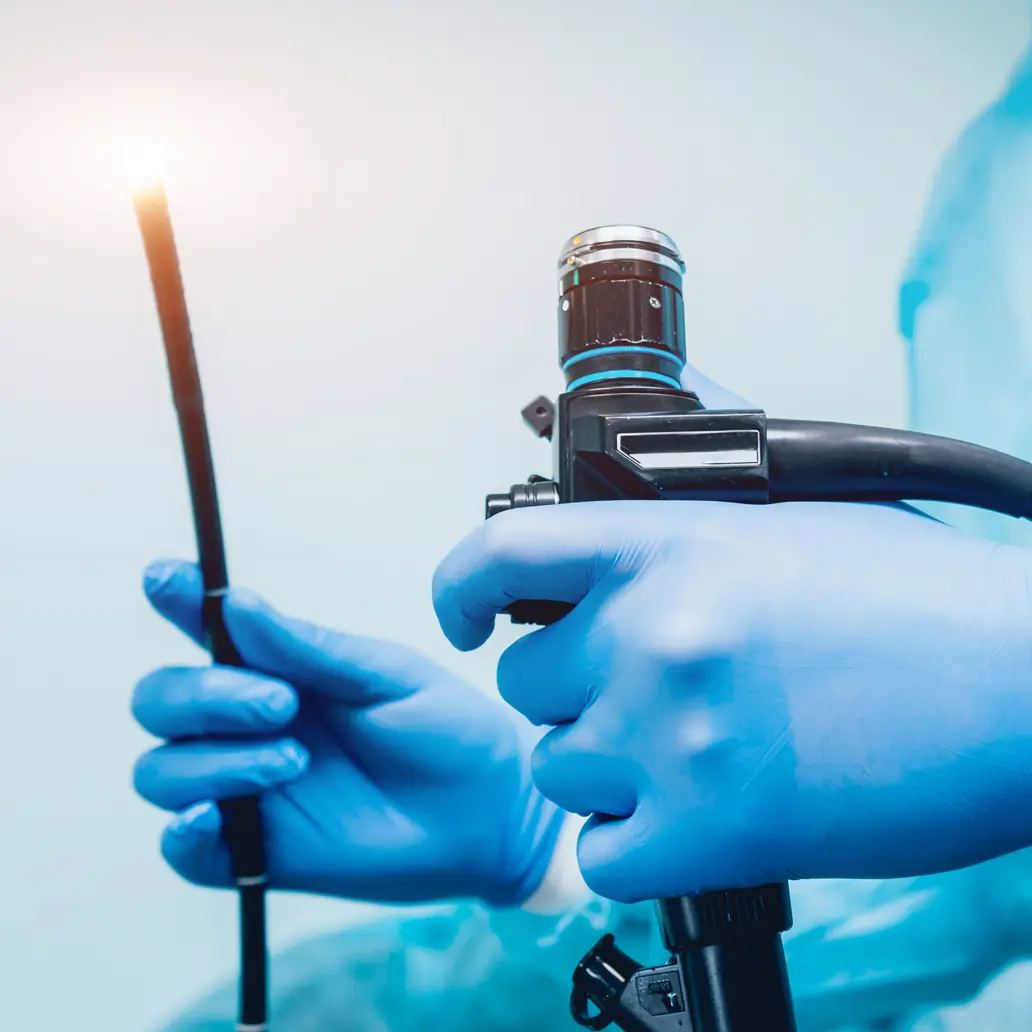
High-level disinfection
Eliminates all microorganisms except for small numbers of bacterial spores. Important for items that come in contact with mucous membrane or nonintact skin, such as endoscopes, ENT scopes, endocavity probes, laryngoscopes and cystoscopes.
Risks associated with improper disinfection or sterilization of equipment include breach of host barriers, person-to-person transmission (e.g. hepatitis B virus) and transmission of environmental pathogens. High-level disinfectants include glutaraldehyde, ortho-phthaladehyde (OPA) accelerated hydrogen peroxide and peracetic acid.
Featured Products
High-level disinfection
Critical surfaces under the Spaulding classification
Medical-surgical devices that enter normally sterile tissue or the vascular system, or through which blood flows, should be sterile because any microbial contamination could transmit disease.
This classification includes the sterilization of surgical instruments, cardiac and urinary catheters, implants and ultrasound probes used in sterile body cavities.
Most of the items in this category should be purchased as sterile or be sterilized. CMS infection control surveys for hospital and ambulatory surgery centers focus on key infection control areas.
To determine compliance with infection control conditions of coverage, surveyors review the cleaning and disinfection protocols used by facilities in each of these areas: precleaning of device or instrument, high-level disinfection protocol, sterilization practice and single-use device reprocessing.
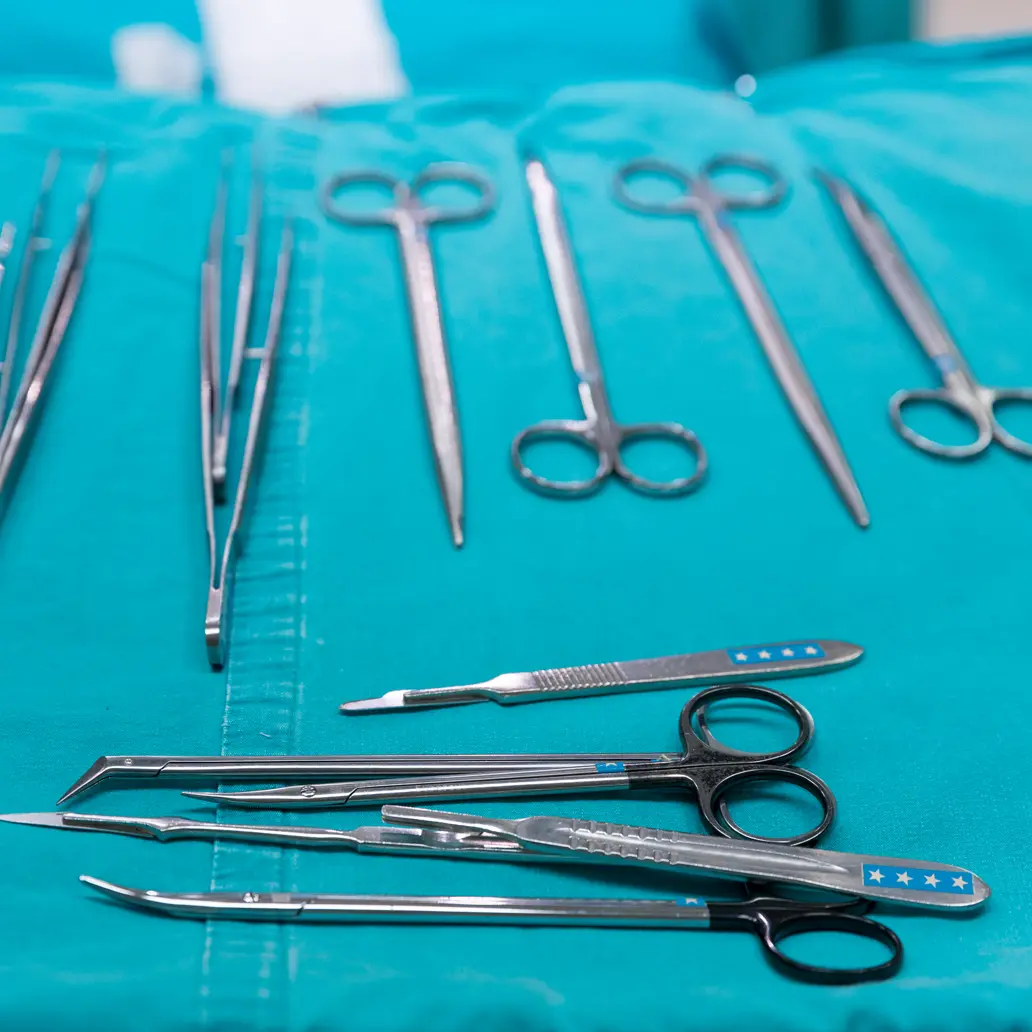
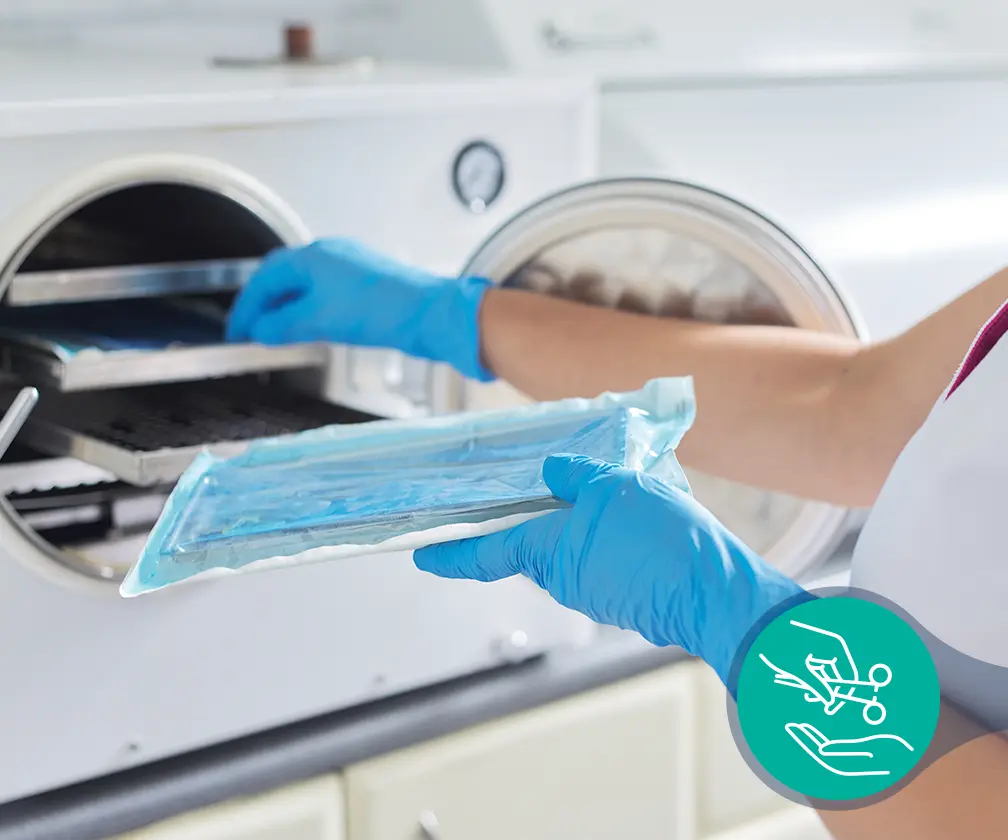
Sterilization
A process that destroys or eliminates all forms of microbial life and is carried out in healthcare facilities by physical or chemical methods. Steam under pressure, dry heat, ethylene oxide gas, hydrogen peroxide gas plasma and liquid chemicals are the principal sterilizing agents used.
Sterility assurance is an important aspect of modern healthcare, as it helps to minimize the patient’s risk for infection at the surgical site. Sterility assurance programs and testing assist users in meeting important quality assurance and CDC requirements.
Before sterilization, items must be cleaned using detergent or enzymatic cleaners. Cleaning should happen as soon as possible after instruments have been used. A manual cleaner or disinfectant ultrasonic washer is very effective in removing microorganisms.
Single-use device reprocessing
Reprocessing single-use devices involves reusing instruments that were designed and sold for single-use only.
These range from external items such as sequential compression device sleeves (SCD) to more invasive devices that include electrothermal equipment, laparoscopic trocars and cannulas that come in contact with blood or human tissue.
Reprocessing of single-use devices must be performed by an FDA-approved reprocessing facility and should not be done in individual facilities.
Featured Products
Sterilization indicators
Sterilization packaging

Our clinical resource team is here to help
Whether you have questions about infection prevention best practices or you need product recommendations, reach out to our dedicated clinical team for support.
1. https://www.cdc.gov/infectioncontrol/pdf/strive/EC101-508.pdf
2. https://www.cdc.gov/infectioncontrol/pdf/outpatient/guide.pdf
3. https://www.cdc.gov/infectioncontrol/guidelines/disinfection/introduction.html
Be advised that information contained herein is intended to serve as a useful reference for informational purposes only and is not complete clinical information. This information is intended for use only by competent healthcare professionals exercising judgment in providing care. McKesson cannot be held responsible for the continued currency of or for any errors or omissions in the information.
The product information contained in this document, including the product images and additional product materials, was collected from various supplier sources. All product claims and specifications are those of the product suppliers and have not been independently verified by McKesson Medical-Surgical or its affiliates (“McKesson”). McKesson is not responsible for errors or omissions in the product information. The properties of a product may change or be inaccurate following the posting or printing of the product information in the document, either in the print or online version. Caution should be exercised when using or purchasing any products from McKesson’s online or print documents by closely examining the product packaging and the labeling prior to use. Due to product changes, information listed in this document is subject to change without notice. This information is placed solely for your convenience in ordering and McKesson disclaims all responsibility for its completeness and accuracy, whether or not the inaccuracy or incompleteness is due to fault or error by McKesson.
©2024 McKesson Medical-Surgical Inc. All trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.